Overload of Glucose Metabolism as Initiating Factor in Diabetic Embryopathy and Prevention by Glyoxalase 1 Inducer Dietary Supplement
by Parri Wentzel, Mingzhan Xue, Naila Rabbani, Ulf J. Eriksson, and Paul J. Thornalley
Abstract
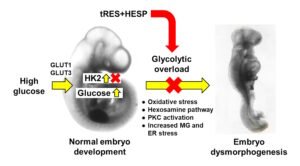
Hyperglycemia in early-stage embryogenesis is linked to diabetic embryopathy. High-glucose-concentration-induced accumulation of hexokinase-2 (HK2) may initiate metabolic dysfunction that contributes to diabetic embryopathy, including increased formation of methylglyoxal (MG). In this study, we evaluated changes in HK2 protein levels and embryo dysmorphogenesis in an experimental model of diabetic embryopathy. Rat embryos were cultured with high glucose concentrations, and the effects of glyoxalase 1 (Glo1) inducer, trans-resveratrol and hesperetin (tRES + HESP) were evaluated. Rat embryos, on gestational day 9, were cultured for 48 h in low and high glucose concentrations with or without tRES + HESP. Embryo crown–rump length, somite number, malformation score, concentrations of HK2 and Glo1 protein, rates of glucose consumption, and MG formation were assessed. Under low-glucose conditions, embryos exhibited normal morphogenesis. In contrast, high-glucose conditions led to reduced crown–rump length and somite number, and an increased malformation score. The addition of 10 μM tRES + HESP reversed these high glucose-induced changes by 60%, 49%, and 47%, respectively. Embryos cultured in high glucose showed increases in HK2 concentration (42%), glucose consumption (75%), and MG formation (27%), normalized to embryo volume. These elevated HK2 levels were normalized by treatment with 10 μM tRES + HESP. Thus, high-glucose-induced metabolic dysfunction and embryopathy may both be initiated by HK2 accumulation and may be preventable with tRES + HESP treatment.
Antioxidants 2025, 14(8), 1022; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14081022
Published: 21 August 2025